What is a CRM?
A CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is a software system designed to help businesses manage and improve their interactions with customers. At its core, a CRM acts as a centralized hub for all customer-related information, enabling businesses to streamline processes, personalize communication, and ultimately, cultivate stronger relationships that drive growth.
Defining CRM and Its Purpose
CRM systems are essentially databases that store and organize customer data, encompassing contact information, purchase history, interactions, and preferences. This data empowers businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their customers, enabling them to tailor their marketing efforts, sales strategies, and customer service interactions for maximum impact.
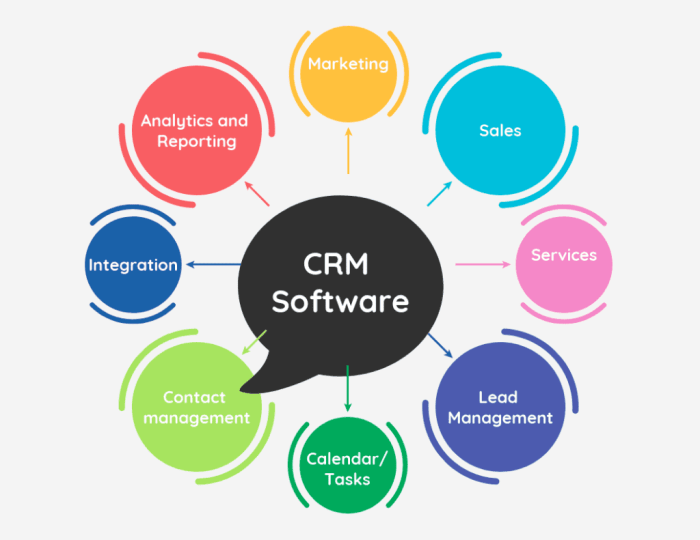
Core Functionalities of a CRM
- Contact Management:Storing and organizing customer information, including contact details, demographics, and communication preferences.
- Sales Automation:Automating sales processes, such as lead generation, qualification, and opportunity management.
- Marketing Automation:Creating and managing targeted marketing campaigns, including email marketing, social media, and website personalization.
- Customer Service Management:Tracking customer support inquiries, resolving issues, and managing customer feedback.
- Reporting and Analytics:Generating insights from customer data to measure campaign performance, identify trends, and make informed business decisions.
Examples of CRM Solutions
The CRM landscape is vast and diverse, offering solutions tailored to different business needs and sizes. Some popular examples include:
- Salesforce:A leading cloud-based CRM platform known for its comprehensive features and scalability.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365:A suite of CRM and ERP solutions integrated with Microsoft’s ecosystem.
- HubSpot:A popular CRM platform for small and medium-sized businesses, known for its user-friendly interface and marketing automation capabilities.
- Zoho CRM:A comprehensive CRM platform with a wide range of features, including sales, marketing, customer service, and project management.
- Pipedrive:A CRM platform focused on sales pipeline management, designed to help businesses visualize and track their sales progress.
Benefits of Using a CRM
Implementing a CRM system offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes, leading to improved customer relationships, increased sales, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Enhanced Customer Relationships
CRM systems empower businesses to build stronger connections with their customers by providing a centralized view of their interactions, preferences, and needs. This enables personalized communication, tailored offers, and proactive customer service, fostering loyalty and satisfaction.
Increased Sales and Revenue
By automating sales processes, streamlining marketing campaigns, and providing valuable insights into customer behavior, CRM systems contribute directly to sales growth and revenue generation. Effective lead nurturing, targeted marketing, and personalized sales pitches all contribute to improved conversion rates and increased revenue.
Examples of CRM Success Stories
Many businesses have successfully leveraged CRM systems to achieve significant improvements in customer engagement and revenue. For instance, a small e-commerce business implemented a CRM to personalize email marketing campaigns, leading to a 20% increase in conversion rates. Similarly, a large retail chain utilized CRM analytics to identify customer segments with high purchase potential, resulting in a 15% boost in sales.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a CRM
Selecting the right CRM system is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Businesses should carefully consider several factors before making a decision, ensuring the chosen solution aligns with their specific needs and goals.
Key Evaluation Factors
- Business Size and Industry:Different CRM systems cater to businesses of varying sizes and industries. Consider the specific features and functionalities required for your business.
- Budget and Cost:CRM solutions come with varying price tags. Evaluate your budget and consider the long-term costs associated with implementation, maintenance, and upgrades.
- Features and Functionality:Assess the features and functionalities offered by different CRM providers, ensuring they align with your business requirements. Consider aspects like contact management, sales automation, marketing automation, customer service management, and reporting and analytics.
- Scalability and Customization:Choose a CRM system that can scale with your business growth and adapt to your evolving needs. Look for customization options to tailor the system to your specific processes and workflows.
- Integration Capabilities:Ensure the CRM can integrate seamlessly with your existing business systems and applications, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms.
- User Friendliness and Support:Select a CRM with a user-friendly interface and comprehensive support resources, including documentation, tutorials, and customer service.
Types of CRM Systems
CRM systems can be categorized based on their deployment model, features, and functionalities. Understanding these different types helps businesses choose the most suitable solution for their specific requirements.
On-Premise CRM
On-premise CRM systems are installed and hosted on a company’s own servers. This provides greater control over data security and customization but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Cloud-Based CRM
Cloud-based CRM systems are hosted on remote servers and accessed via the internet. They offer greater flexibility, scalability, and affordability compared to on-premise solutions. Cloud-based CRMs are typically subscription-based, with costs varying depending on the features and functionalities chosen.
Open-Source CRM
Open-source CRM systems are freely available for download and modification. This provides businesses with greater control over the software and the ability to customize it to their specific needs. However, open-source CRMs may require technical expertise for implementation and maintenance.
Comparison Table
| Type | Deployment | Cost | Customization | Scalability | Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Premise | Company Servers | High (Upfront Investment) | High | Moderate | High |
| Cloud-Based | Remote Servers | Subscription-Based | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Open-Source | Freely Available | Free (Initial Download) | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Popular CRM Platforms
The CRM market is highly competitive, with numerous platforms vying for market share. Here’s a look at some of the top-rated CRM solutions available today.
Top-Rated CRM Platforms
- Salesforce:A leading cloud-based CRM platform known for its comprehensive features, scalability, and robust ecosystem of integrations. It offers a wide range of solutions for different industries and business sizes.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365:A suite of CRM and ERP solutions integrated with Microsoft’s ecosystem. It provides a comprehensive platform for managing sales, marketing, customer service, and operations.
- HubSpot:A popular CRM platform for small and medium-sized businesses, known for its user-friendly interface and marketing automation capabilities. It offers a free plan for basic CRM functionalities and paid plans for advanced features.
- Zoho CRM:A comprehensive CRM platform with a wide range of features, including sales, marketing, customer service, and project management. It offers a variety of plans to suit different business needs and budgets.
- Pipedrive:A CRM platform focused on sales pipeline management, designed to help businesses visualize and track their sales progress. It offers a simple and intuitive interface that makes it easy to manage leads and opportunities.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Each CRM platform has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice for a particular business depends on its specific needs and priorities. For example, Salesforce is known for its comprehensive features and scalability but can be expensive, while HubSpot is more affordable but may lack some of the advanced features offered by Salesforce.
Real-World Examples
Many businesses have successfully implemented these CRM platforms to improve their customer relationships and drive growth. For instance, a small startup used HubSpot to automate its email marketing campaigns, leading to a significant increase in leads and sales. A large enterprise, on the other hand, chose Salesforce to manage its global customer base, leveraging its robust features and scalability to streamline its operations.
CRM Implementation and Integration
Successfully implementing a CRM system requires careful planning and execution. Businesses need to consider data migration, user training, and integration with existing systems to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the CRM.
Implementation Process

- Planning and Requirements Gathering:Define your business goals and objectives for implementing a CRM. Identify the specific features and functionalities required to achieve these goals.
- Data Migration:Transfer your existing customer data from legacy systems to the CRM platform. Ensure data accuracy and completeness during the migration process.
- User Training:Provide comprehensive training to your employees on how to use the CRM effectively. This includes familiarizing them with the interface, functionalities, and best practices.
- Testing and Deployment:Test the CRM system thoroughly before deploying it to your entire organization. This ensures that the system is working as expected and meets your business requirements.
Integration with Other Systems
Integrating the CRM with other business systems, such as email marketing platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce platforms, is crucial for streamlining workflows and improving data consistency. This allows for seamless data flow between different systems, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
CRM Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of a CRM system, businesses should adopt best practices for data management, lead nurturing, and customer engagement.
Data Management

- Data Accuracy and Completeness:Ensure that customer data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. This involves implementing data validation rules and processes for data entry and updates.
- Data Segmentation:Segment your customer base based on demographics, purchase history, and other relevant criteria. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns and personalized communication.
- Data Security:Implement robust security measures to protect customer data from unauthorized access and breaches. This includes using strong passwords, encryption, and access controls.
Lead Nurturing
- Lead Scoring:Assign scores to leads based on their engagement and potential value. This helps prioritize leads and allocate resources effectively.
- Automated Email Sequences:Create automated email sequences to nurture leads and guide them through the sales funnel. These sequences can provide valuable information, answer common questions, and build relationships.
- Personalized Content:Deliver personalized content based on lead interests and preferences. This increases engagement and improves the chances of conversion.
Customer Engagement
- Personalized Communication:Use the CRM to personalize communication with customers, addressing them by name, referring to their past interactions, and offering relevant recommendations.
- Proactive Customer Service:Use the CRM to track customer interactions and identify potential issues. This allows for proactive customer service and prevents problems from escalating.
- Customer Feedback:Regularly collect customer feedback to understand their satisfaction levels and identify areas for improvement. This can be done through surveys, reviews, and social media monitoring.
CRM Analytics
Leverage CRM analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, track campaign performance, and optimize business operations. Analyze data on lead generation, conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and other key metrics to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions.
The Future of CRM
The CRM landscape is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, changing customer expectations, and emerging business trends. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and other innovative technologies are playing a significant role in shaping the future of CRM.
Emerging Trends
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI is transforming CRM by automating tasks, providing personalized recommendations, and improving customer service. AI-powered chatbots, for example, can handle customer inquiries and provide instant support.
- Machine Learning (ML):ML algorithms are used to analyze customer data and predict future behavior. This enables businesses to personalize marketing campaigns, identify potential churn, and offer proactive customer service.
- Customer Experience (CX):CX is becoming increasingly important, and CRM systems are evolving to support a more holistic approach to customer engagement. This includes integrating CRM with other CX technologies, such as social media monitoring and sentiment analysis.
The Role of AI and ML
AI and ML are transforming CRM by enabling businesses to automate tasks, personalize communication, and gain deeper insights into customer behavior. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for more complex tasks. ML algorithms can analyze customer data to predict future behavior, enabling businesses to personalize marketing campaigns and offer proactive customer service.
Predictions for the Future
The future of CRM is bright, with continued advancements in AI, ML, and other technologies driving innovation and improving customer experiences. We can expect to see more personalized and proactive CRM solutions, with a focus on omnichannel engagement and data-driven insights.