Understanding Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is crucial in assessing the effectiveness and success of any business. These metrics provide valuable insights into various aspects of business operations, allowing organizations to track progress towards their goals and objectives. This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, importance, functions, types, and implementation tips of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), shedding light on their significance in optimizing business performance. Let’s explore the world of KPIs and uncover how they can propel your business towards greater success.
Definition and Importance of KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics used to evaluate a company’s performance in achieving its strategic objectives. These indicators act as crucial measurement tools, providing insights into how effectively an organization is progressing towards its goals. By setting and monitoring KPIs, businesses can quantitatively assess their success and make informed decisions to drive continuous improvement.
Tracking Key Performance Indicators KPIs on a regular basis, whether daily, weekly, or monthly, allows businesses to stay agile and responsive to changing market conditions. The data derived from KPIs not only reflects goal achievement but also reveals areas for refinement and enhancement. This real-time monitoring empowers managers to identify trends early, proactively address issues, and capitalize on opportunities, contributing to sustained business growth and competitiveness.

Functions of KPIs
KPIs play a crucial role in enhancing business performance by promoting transparency through evaluating both employee and business performance. By providing concrete data-driven insights, Key Performance Indicators KPIs enable organizations to make informed decisions and monitor progress effectively.
One of the primary functions of KPIs is to measure performance comprehensively, allowing businesses to track their advancement towards predefined targets. By setting clear and measurable KPIs, organizations can gauge their success and areas needing improvement, facilitating strategic planning and decision-making.
Key Performance Indicators KPIs serve as powerful tools for employee motivation by offering structured performance feedback and aligning individual objectives with company standards. By establishing KPIs that reflect organizational goals, companies can inspire and engage their workforce, driving productivity and commitment.
Furthermore, KPIs aid in honing employee skills by assessing enhancements and identifying areas for development. Through the evaluation of key metrics related to employee performance, organizations can design targeted training programs, fostering continuous learning and growth within the workforce.
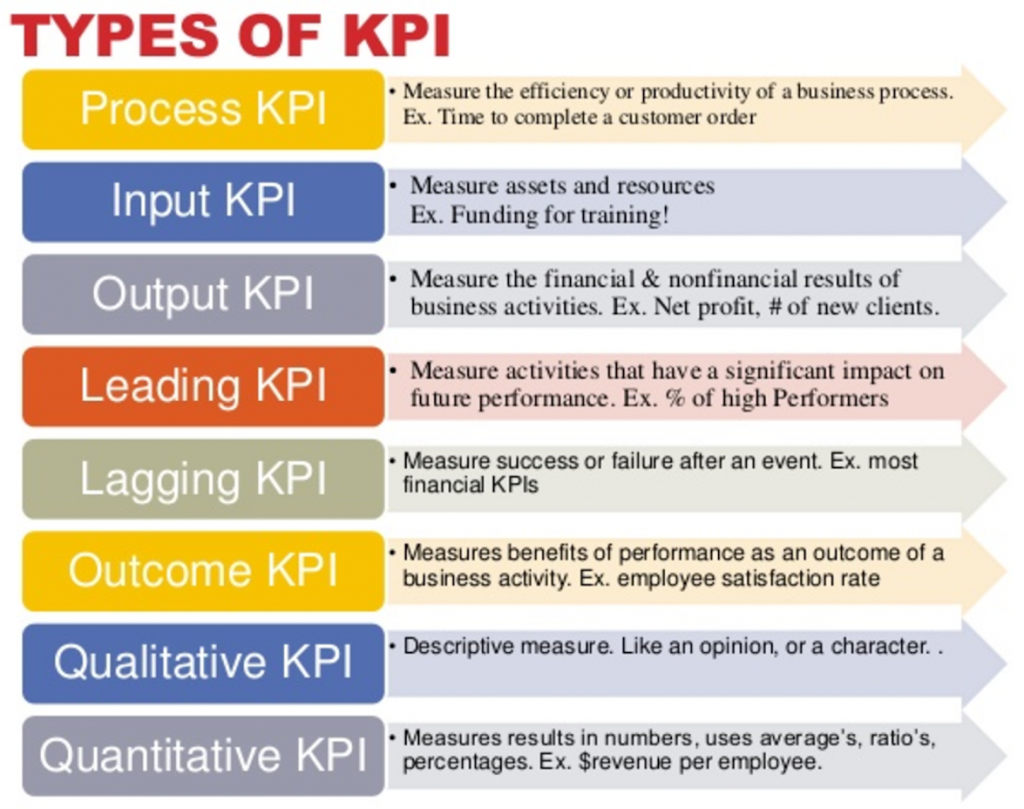
Types of KPIs
Financial Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) focus on the monetary aspects of a business, providing crucial insights into its financial health. Metrics like gross profit margins and current ratios fall under this category, offering a clear picture of profitability and liquidity.
Non-Financial KPIs, although not directly linked to financial figures, play a significant role in shaping a company’s overall performance. These indicators, encompassing customer satisfaction levels and market share, contribute to long-term success by gauging customer loyalty and market competitiveness.

Tips for Implementing KPIs (SMART)
When defining Key Performance Indicators KPIs, clarity is crucial. Ensure that each KPI is specific, leaving no room for ambiguity. Define precisely what will be measured to track progress effectively and make informed decisions based on the outcomes obtained.
Implementing KPIs requires setting measurable targets that are achievable by all stakeholders involved. This ensures that everyone understands what is expected and can contribute effectively towards reaching the established goals. Measurable KPIs help in monitoring performance and evaluating success impartially.
An important aspect of KPI implementation is ensuring that the chosen indicators are achievable within the defined standards. This means that the metrics selected should be realistic, attainable, and within reach based on the resources and capabilities of the organization. Setting achievable KPIs promotes continuous improvement and motivates teams to excel.
For KPIs to drive meaningful outcomes, they must be directly relevant to the business’s vision and mission. Aligning KPIs with the overall objectives of the organization provides a clear direction for efforts and resources, ensuring that all activities contribute to the strategic goals set by the company. Relevant KPIs guide decision-making and resource allocation effectively.
Time-bound KPIs come with clear deadlines for achievement, fostering a sense of urgency and accountability within the organization. Establishing time-bound targets helps in prioritizing tasks, managing resources efficiently, and tracking progress over specific periods. Time-bound KPIs create a sense of focus and drive towards meeting objectives within defined timeframes.
Calculation Methods of KPIs
When evaluating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), it’s crucial to understand that lower scores often signify better performance. For instance, in metrics like employee turnover rates, a lower score indicates a positive outcome, reflecting higher employee retention and satisfaction levels.
In determining the most suitable formulas for KPI calculations, focus on selecting formulas that offer valuable and relevant insights into the specific aspect of performance being measured. The chosen formulas should align with the objectives and goals set for the KPI, ensuring that the generated data accurately represents the performance indicator’s effectiveness.
Examples of KPIs
In the realm of financial KPIs, tracking metrics such as total revenue, net income, and debt-to-equity ratio can provide crucial insights into the financial health and performance of a business. These indicators serve as vital benchmarks for assessing profitability, financial efficiency, and overall sustainability, thus guiding strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
When it comes to production KPIs, monitoring product quality levels, yield rates, and loading time is essential for evaluating operational efficiency and performance. By setting and tracking these key indicators, businesses can ensure consistent product quality, optimize production processes, and minimize downtime, ultimately enhancing productivity and competitiveness in the market.
In the dynamic landscape of marketing, focusing on KPIs like conversion rates, generated prospect numbers, and market share offers valuable insights into the effectiveness of marketing activities and campaigns. These indicators help businesses gauge customer engagement, campaign success, and competitive positioning, enabling them to fine-tune marketing strategies, allocate resources efficiently, and drive growth in target markets.
