Introduction to Microsoft CRM Software
Microsoft CRM, also known as Dynamics 365 Sales, is a comprehensive customer relationship management (CRM) software solution designed to help businesses manage and improve their interactions with customers. It offers a wide range of features and functionalities that streamline sales processes, automate tasks, and provide valuable insights into customer behavior.
Microsoft CRM aims to empower businesses to build stronger customer relationships, increase sales, and ultimately drive revenue growth.
Key Features and Functionalities
Microsoft CRM boasts a comprehensive set of features that cater to various aspects of customer relationship management. These features include:
- Contact Management:Organize and manage customer information, including contact details, communication history, and purchase records.
- Lead Management:Track and nurture potential leads, identify promising prospects, and prioritize follow-up efforts.
- Opportunity Management:Manage sales opportunities, track progress, and forecast revenue based on potential deals.
- Sales Automation:Automate repetitive tasks such as sending emails, scheduling appointments, and generating quotes.
- Marketing Automation:Create targeted marketing campaigns, track campaign performance, and personalize customer interactions.
- Customer Service:Manage customer support inquiries, track case resolutions, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Reporting and Analytics:Gain insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness through comprehensive reports and dashboards.
- Mobile Access:Access and manage CRM data from any device, ensuring seamless communication and collaboration.
History of Microsoft CRM
Microsoft CRM has a rich history, evolving over time to meet the changing needs of businesses. Its origins can be traced back to the early 2000s with the release of Microsoft CRM 1. 0. Since then, Microsoft has consistently updated and enhanced the software, incorporating new features and technologies to stay ahead of the curve in the CRM landscape.
Key milestones in Microsoft CRM’s evolution include:
- 2003:Microsoft CRM 1.2 was released, introducing key features like sales automation and customer service capabilities.
- 2006:Microsoft CRM 3.0 brought significant enhancements, including marketing automation and improved reporting functionalities.
- 2011:Microsoft CRM 2011 introduced a more user-friendly interface and cloud-based deployment options.
- 2013:Microsoft CRM 2013 focused on social media integration and mobile accessibility, aligning with the growing importance of digital channels.
- 2016:Microsoft Dynamics 365 was launched, unifying CRM and ERP solutions under a single platform.
Benefits of Using Microsoft CRM Software
Implementing Microsoft CRM can bring numerous benefits to businesses, enhancing their customer relationship management practices and driving positive outcomes. These benefits include:
Improved Customer Relationship Management
Microsoft CRM empowers businesses to centralize customer information, streamline interactions, and personalize communication, leading to improved customer relationships. By providing a comprehensive view of customer data, including past interactions, purchase history, and preferences, Microsoft CRM enables businesses to understand their customers better and tailor their approach accordingly.
This personalized approach fosters customer loyalty and satisfaction, leading to increased retention rates and repeat business.
Increased Sales and Revenue
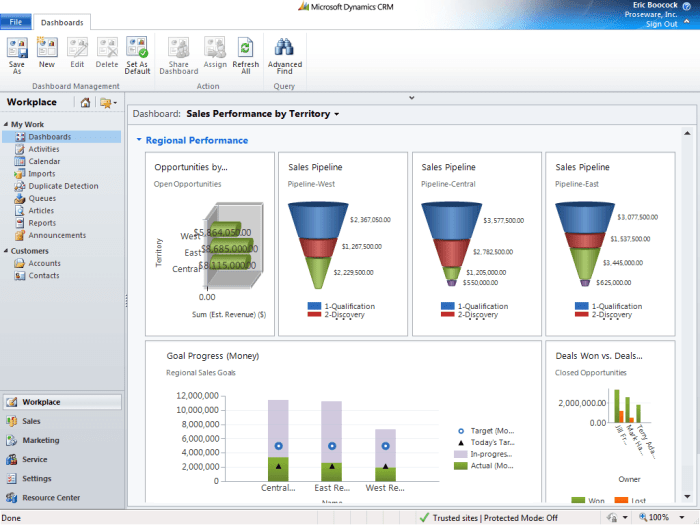
Microsoft CRM’s sales automation features streamline sales processes, allowing sales teams to focus on high-value activities like prospecting and closing deals. By automating repetitive tasks, Microsoft CRM frees up valuable time for sales representatives to engage with customers, build rapport, and ultimately drive sales.
The software’s lead management and opportunity tracking features help identify promising prospects, prioritize sales efforts, and maximize revenue generation.
Enhanced Customer Service
Microsoft CRM’s customer service features empower businesses to provide efficient and effective support to their customers. The software allows businesses to track customer inquiries, manage case resolutions, and monitor customer satisfaction levels. This enables businesses to identify and address customer issues promptly, minimizing frustration and maximizing customer satisfaction.
By providing exceptional customer service, businesses can build strong customer relationships and retain valuable clients.
Examples of Businesses Benefiting from Microsoft CRM
Numerous businesses across various industries have successfully implemented Microsoft CRM, experiencing significant improvements in their customer relationship management practices and business outcomes. For example, a leading retail chain leveraged Microsoft CRM to centralize customer data, personalize marketing campaigns, and optimize customer service efforts.
This resulted in a 15% increase in customer retention and a 10% rise in sales revenue. Similarly, a financial services company implemented Microsoft CRM to streamline lead generation, improve sales forecasting, and enhance customer communication. This resulted in a 20% reduction in sales cycle time and a 15% increase in conversion rates.
Key Components of Microsoft CRM
Microsoft CRM is composed of various modules, each designed to address specific aspects of customer relationship management. These modules work together seamlessly to create a comprehensive CRM solution that caters to the diverse needs of businesses.
Core Modules and Their Functions
The core modules of Microsoft CRM include:
- Sales:This module focuses on managing sales processes, from lead generation to closing deals. It provides tools for tracking leads, managing opportunities, forecasting revenue, and automating sales tasks.
- Marketing:This module enables businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns, automate marketing tasks, and track campaign performance. It includes features for email marketing, social media marketing, and event management.
- Customer Service:This module helps businesses manage customer support inquiries, track case resolutions, and improve customer satisfaction. It provides tools for managing cases, knowledge bases, and customer feedback.
- Field Service:This module is designed for businesses that provide field service operations. It enables businesses to schedule appointments, track technicians, and manage service requests.
- Project Service Automation:This module helps businesses manage project-based work, from planning and budgeting to resource allocation and billing.
How Modules Work Together
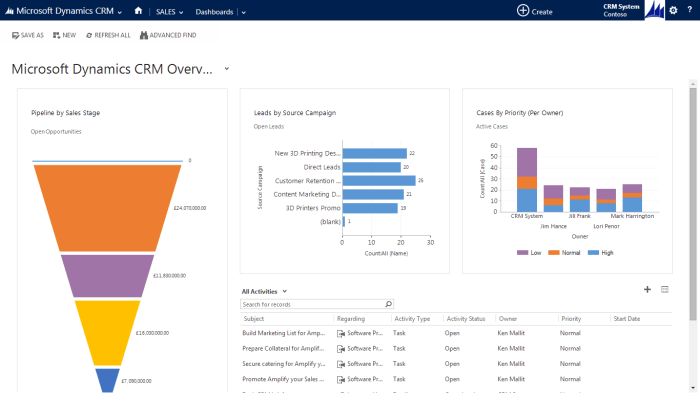
The modules in Microsoft CRM are interconnected, allowing data to flow seamlessly between them. For example, a lead generated through a marketing campaign can be automatically transferred to the sales module, where it can be assigned to a sales representative for follow-up.
Similarly, a customer service case can be created based on information gathered from the sales module, ensuring a consistent customer experience across different departments. This integrated approach enables businesses to gain a comprehensive view of their customers and optimize their CRM processes.
Table Showcasing Key Features and Benefits
| Module | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sales | Lead management, opportunity tracking, sales automation, forecasting | Improved sales efficiency, increased conversion rates, better revenue forecasting |
| Marketing | Campaign management, marketing automation, email marketing, social media marketing | Targeted marketing efforts, improved campaign performance, increased customer engagement |
| Customer Service | Case management, knowledge base, customer feedback, service level agreements | Enhanced customer support, faster resolution times, improved customer satisfaction |
| Field Service | Appointment scheduling, technician tracking, service request management | Optimized field service operations, improved technician productivity, enhanced customer service |
| Project Service Automation | Project planning, budgeting, resource allocation, billing | Improved project management, increased profitability, enhanced customer satisfaction |
Implementing Microsoft CRM
Implementing Microsoft CRM requires a strategic approach to ensure a successful transition and maximize its benefits. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing Microsoft CRM in a business:
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
- Define Business Requirements:Identify the specific needs and objectives of the business. What are the key challenges to be addressed? What are the desired outcomes of implementing Microsoft CRM?
- Choose the Right Deployment Option:Microsoft CRM offers different deployment options, including on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid. Choose the option that best aligns with the business’s infrastructure and security requirements.
- Configure Microsoft CRM:Customize the software to meet the specific needs of the business. This includes configuring modules, workflows, and reports.
- Data Migration:Transfer existing customer data from legacy systems to Microsoft CRM. Ensure data accuracy and completeness during migration.
- User Training:Provide comprehensive training to users on how to effectively utilize Microsoft CRM. This ensures user adoption and maximizes the software’s benefits.
- Go Live and Monitor Performance:Launch Microsoft CRM and monitor its performance closely. Identify any areas for improvement and make adjustments as needed.
Deployment Options for Microsoft CRM
Microsoft CRM offers three primary deployment options:
- On-premises:Microsoft CRM is installed and hosted on the business’s own servers. This provides greater control over data security and customization but requires significant infrastructure investment.
- Cloud-based:Microsoft CRM is hosted on Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure. This eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and offers scalability and flexibility. It also requires less upfront investment but involves monthly subscription fees.
- Hybrid:This combines on-premises and cloud-based deployments, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both options. It offers greater flexibility and customization but requires careful planning and management.
Tips and Best Practices for Successful CRM Implementation
To ensure a successful Microsoft CRM implementation, consider these tips and best practices:
- Involve Key Stakeholders:Engage representatives from different departments to gather input and ensure alignment with business needs.
- Start Small and Scale Gradually:Begin with a pilot project involving a small group of users and gradually expand the implementation as the system is proven effective.
- Prioritize Data Quality:Ensure accurate and complete data migration to maximize the benefits of Microsoft CRM.
- Provide Ongoing Support:Offer continuous training and support to users to ensure they can effectively utilize Microsoft CRM.
- Monitor and Evaluate Performance:Regularly review the performance of Microsoft CRM and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
Integrating Microsoft CRM with Other Systems
Integrating Microsoft CRM with other business systems is crucial for creating a unified and efficient workflow. By connecting Microsoft CRM with other software applications, businesses can streamline data flow, eliminate manual data entry, and enhance overall productivity.
Importance of Integration
Integrating Microsoft CRM with other systems offers numerous benefits, including:
- Data Consistency:Eliminates data silos and ensures consistent data across different systems, reducing errors and improving decision-making.
- Improved Workflow:Automates data transfer between systems, streamlining processes and reducing manual effort.
- Enhanced Collaboration:Enables seamless information sharing between teams, fostering better communication and collaboration.
- Increased Efficiency:Automates tasks and eliminates redundant data entry, freeing up time for more strategic activities.
Integrating Microsoft CRM with Microsoft Office 365
Microsoft CRM seamlessly integrates with Microsoft Office 365, providing a unified platform for communication, collaboration, and productivity. This integration enables businesses to:
- Share CRM data with Office 365 users:Access customer information and sales data directly within Outlook, Word, and Excel.
- Automate email marketing campaigns:Leverage Microsoft CRM’s marketing automation features within Outlook to create and manage email campaigns.
- Schedule appointments and meetings:Integrate Microsoft CRM with Outlook calendar to schedule appointments and meetings with customers.
- Collaborate on sales documents:Share and co-edit sales proposals and presentations within Microsoft CRM using OneDrive and SharePoint.
Examples of Successful Integrations
Many businesses have successfully integrated Microsoft CRM with other systems, achieving significant improvements in their operations. For instance, a manufacturing company integrated Microsoft CRM with its enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, streamlining order processing and inventory management. This integration resulted in a 15% reduction in order fulfillment time and a 10% decrease in inventory costs.
Similarly, a healthcare provider integrated Microsoft CRM with its electronic health records (EHR) system, improving patient engagement and communication. This integration led to a 20% increase in patient satisfaction and a 15% reduction in administrative costs.
Customization and Configuration of Microsoft CRM
Microsoft CRM offers a high degree of customization and configuration options, allowing businesses to tailor the software to their specific needs. This flexibility ensures that Microsoft CRM can adapt to the unique requirements of different industries and business models.
Customization Options
Microsoft CRM provides various customization options, including:
- Custom Fields:Add custom fields to existing entities (e.g., contacts, leads, opportunities) to store additional information relevant to the business.
- Custom Entities:Create new entities to represent unique data structures that are not included in the standard Microsoft CRM entities.
- Custom Views:Define custom views to filter and display data in a way that is most relevant to specific users or departments.
- Custom Forms:Modify the layout and fields displayed on forms to optimize user experience and data collection.
- Custom Workflows:Automate business processes by creating custom workflows that trigger specific actions based on predefined conditions.
Configuring Microsoft CRM to Meet Specific Business Needs
Businesses can configure Microsoft CRM to meet their specific needs by:
- Defining Security Roles:Assign different levels of access and permissions to users based on their roles and responsibilities within the organization.
- Customizing Dashboards:Create personalized dashboards that display key performance indicators (KPIs) and relevant data for different users.
- Setting up Business Rules:Define rules that automatically trigger specific actions based on predefined conditions, such as sending notifications or updating records.
- Implementing Custom Integrations:Connect Microsoft CRM with other business systems using APIs and connectors to streamline data flow and automate processes.
Examples of Customized Workflows and Reports
A real estate company customized Microsoft CRM to automate the process of generating property listings. When a new property is added to the system, a workflow automatically generates a property listing with relevant details and images, which is then sent to the company’s website and social media platforms.
This automation saves significant time and effort, ensuring consistent and timely property listings. Similarly, a manufacturing company customized Microsoft CRM to create a report that tracks the performance of different sales teams. The report displays key metrics such as revenue generated, conversion rates, and customer satisfaction scores, allowing the company to identify areas for improvement and optimize sales strategies.
Microsoft CRM and Data Security
Data security is paramount in CRM software, as it handles sensitive customer information. Microsoft CRM implements robust security measures to protect customer data and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Data Security Measures
Microsoft CRM employs various data security measures, including:
- Data Encryption:Customer data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, protecting it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control:Users are granted access only to the data they need, based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Multi-factor Authentication:Users must provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code, to access the system.
- Regular Security Audits:Microsoft regularly audits its systems and infrastructure to identify and address potential security vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Certifications:Microsoft CRM meets industry-standard compliance certifications, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2, demonstrating its commitment to data security and privacy.
Importance of Data Privacy and Compliance
Data privacy and compliance are essential for building trust with customers and maintaining a positive reputation. By adhering to regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), businesses can ensure they are handling customer data responsibly and ethically.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Customer Data
To further protect sensitive customer data in Microsoft CRM, businesses should follow these best practices:
- Train Employees on Data Security:Educate employees on data security policies and best practices to minimize the risk of data breaches.
- Implement Strong Password Policies:Encourage users to create strong passwords and change them regularly.
- Limit Data Access:Grant access to data only on a need-to-know basis.
- Regularly Backup Data:Create regular backups of customer data to ensure data recovery in case of a security incident.
- Monitor for Suspicious Activity:Implement monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activity within the CRM system.