Company Overview
Chevron Corporation, commonly known as Chevron, is an American multinational energy corporation headquartered in San Ramon, California. With a rich history dating back to the late 19th century, Chevron has evolved into one of the world’s leading integrated energy companies.
History and Background
Chevron’s roots can be traced back to the Standard Oil Company, founded by John D. Rockefeller in 1870. Through mergers and acquisitions over the years, Chevron’s predecessors, including Standard Oil of California and Gulf Oil, eventually merged to form Chevron in 1984.
Core Business Activities and Segments
Chevron’s core business activities encompass the exploration, production, refining, marketing, and transportation of oil and natural gas. The company operates in various segments, including:
- Upstream:Exploration and production of oil and natural gas, including activities in both conventional and unconventional resources.
- Downstream:Refining crude oil into petroleum products, marketing and distributing refined products, and operating chemical plants.
- Midstream:Transportation and storage of oil and natural gas, including pipelines, terminals, and other infrastructure.
Geographic Footprint and Key Markets
Chevron has a global presence, operating in numerous countries across North America, South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa. Key markets for Chevron include the United States, Canada, Brazil, Australia, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, and the United Kingdom.
Mission, Vision, and Values
Chevron’s mission is to be a leading energy company that provides affordable, reliable, and ever-cleaner energy solutions. The company’s vision is to be the global leader in integrated energy, while its values emphasize safety, integrity, respect, and excellence.
Financial Performance
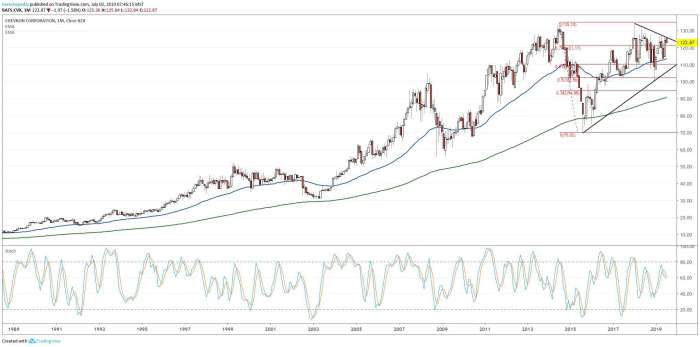
Chevron’s financial performance is a key indicator of its overall health and profitability. The company’s recent financial results have been influenced by various factors, including global oil and gas prices, economic conditions, and operational efficiency.
Revenue, Earnings, and Cash Flow
Chevron’s revenue is primarily derived from the sale of oil and natural gas, as well as refined products and chemicals. The company’s earnings have fluctuated in recent years, reflecting the volatility of energy prices. Cash flow is a crucial metric for Chevron, as it allows the company to invest in exploration, production, and other capital projects.
Key Financial Metrics
- Profitability:Measured by metrics such as return on equity (ROE) and return on assets (ROA), Chevron’s profitability has generally been strong, reflecting its efficient operations and scale.
- Liquidity:Chevron’s strong financial position allows it to maintain healthy liquidity ratios, indicating its ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Leverage:Chevron’s debt levels have remained manageable, demonstrating a prudent approach to financial risk management.
Comparison to Industry Peers
Chevron’s financial performance is often compared to its industry peers, such as ExxonMobil, BP, and Shell. These comparisons provide insights into Chevron’s relative strengths and weaknesses within the global oil and gas sector.
Trends and Patterns
Analyzing Chevron’s financial performance over time reveals trends and patterns. For example, the company’s revenue and earnings have historically been cyclical, influenced by factors such as oil prices and global economic growth.
Industry Outlook
The global oil and gas industry is a dynamic and complex sector, facing a range of challenges and opportunities. Understanding the current state of the industry is essential for assessing Chevron’s future prospects.
Current State of the Industry
The oil and gas industry is undergoing a period of significant transformation, driven by factors such as technological advancements, environmental concerns, and geopolitical shifts. The industry is facing increasing pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and transition towards cleaner energy sources.
Key Drivers and Challenges
- Energy Demand:Global energy demand is expected to continue growing, driven by population growth and economic development, although the pace of growth may vary depending on factors such as technological advancements and policy changes.
- Climate Change:The oil and gas industry is facing increasing scrutiny over its environmental impact, particularly its contribution to climate change. Governments and investors are increasingly demanding that energy companies reduce their emissions and transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements, such as hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling, have led to a surge in unconventional oil and gas production. However, these technologies also raise environmental concerns and have implications for the industry’s future.
- Geopolitical Factors:Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can impact oil and gas prices and production. For example, the war in Ukraine has led to uncertainty in global energy markets.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities
- Renewable Energy:The oil and gas industry is increasingly investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal, as a way to diversify their portfolios and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Carbon Capture and Storage:Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies have the potential to reduce emissions from fossil fuel power plants and industrial facilities. The oil and gas industry is playing a role in developing and deploying CCS technologies.
- Hydrogen:Hydrogen is emerging as a potential clean energy source. The oil and gas industry is well-positioned to play a role in the production and distribution of hydrogen.
Impact of Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies are playing an increasingly important role in shaping the future of the oil and gas industry. Governments around the world are implementing policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote renewable energy, and ensure energy security.
Investment Analysis
Investing in Chevron involves considering the company’s current valuation, potential risks and opportunities, and its dividend policy. Investors also need to compare Chevron’s investment potential to other energy companies.
Current Valuation and Risk/Opportunity Analysis
Chevron’s valuation is influenced by factors such as oil and gas prices, production levels, and the company’s financial performance. Investors need to assess the company’s intrinsic value and compare it to its current market price. Potential risks include volatility in energy prices, environmental regulations, and competition.
Opportunities include potential growth in oil and gas demand, technological advancements, and diversification into renewable energy.
Dividend Policy and Shareholder Returns
Chevron has a long history of paying dividends to its shareholders. The company’s dividend policy is designed to provide a steady stream of income to investors. Shareholder returns are also influenced by factors such as stock price appreciation and share buybacks.
Comparison to Other Energy Companies
Investors often compare Chevron’s investment potential to other energy companies, such as ExxonMobil, BP, and Shell. These comparisons provide insights into Chevron’s relative strengths and weaknesses in terms of valuation, growth prospects, and dividend yields.
Potential Future Growth Drivers
Potential future growth drivers for Chevron include:
- Increased Global Energy Demand:As the global economy grows, demand for energy is expected to increase, creating opportunities for oil and gas producers.
- Technological Advancements:Chevron is investing in technologies that can enhance its efficiency and reduce its environmental impact, such as carbon capture and storage and renewable energy.
- Diversification into Renewable Energy:Chevron is expanding into renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to diversify its portfolio and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
ESG Considerations
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are becoming increasingly important for investors. Companies are being held accountable for their environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices.
ESG Performance
Chevron’s ESG performance is a key consideration for investors. The company has made progress in areas such as reducing its greenhouse gas emissions, promoting diversity and inclusion, and improving its corporate governance practices. However, Chevron faces challenges in addressing concerns about its environmental impact, particularly its role in climate change.
Climate Change
Chevron is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions and developing cleaner energy solutions. The company has set targets for reducing emissions and is investing in technologies such as carbon capture and storage and renewable energy.
Social Responsibility
Chevron is committed to operating responsibly in the communities where it operates. The company focuses on initiatives such as promoting economic development, supporting education, and improving healthcare.
Corporate Governance
Chevron has a strong corporate governance framework that emphasizes transparency, accountability, and ethical conduct. The company’s board of directors is responsible for overseeing the company’s operations and ensuring that it meets its ESG commitments.
Comparison to Industry Peers
Chevron’s ESG performance is often compared to its industry peers. These comparisons provide insights into Chevron’s relative strengths and weaknesses in areas such as environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance.
ESG Risks and Opportunities
Chevron faces potential ESG risks, such as regulatory scrutiny, investor activism, and reputational damage. However, the company also has opportunities to enhance its ESG performance and capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Competitor Analysis
Chevron operates in a competitive industry, facing competition from other major oil and gas companies. Understanding Chevron’s key competitors is essential for assessing its market position and future growth prospects.
Key Competitors
Chevron’s key competitors in the oil and gas industry include ExxonMobil, BP, Shell, TotalEnergies, and ConocoPhillips. These companies compete with Chevron in various aspects of the industry, including exploration and production, refining, marketing, and transportation.
Comparison of Business Models, Strategies, and Performance
Each of Chevron’s competitors has its own unique business model, strategies, and performance. For example, ExxonMobil has a strong focus on upstream operations, while BP has a more diversified portfolio that includes renewable energy. Comparing these companies allows investors to understand Chevron’s relative strengths and weaknesses.
Competitive Advantages and Disadvantages
Chevron has several competitive advantages, including its global scale, strong financial position, and technological expertise. However, the company also faces some disadvantages, such as its environmental record and its reliance on fossil fuels.
Impact of Competition on Future Growth Prospects
Competition in the oil and gas industry is intense, and it is likely to intensify in the future as the industry transitions to a low-carbon economy. Chevron’s ability to compete effectively will depend on its ability to adapt to changing market conditions and invest in technologies that can reduce its environmental impact.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are transforming the oil and gas industry, creating both opportunities and challenges for companies like Chevron. Understanding the impact of these advancements is essential for assessing Chevron’s future prospects.
Impact on the Oil and Gas Industry
Technological advancements are having a profound impact on the oil and gas industry. For example, hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and horizontal drilling have revolutionized unconventional oil and gas production. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to improve exploration, production, and efficiency.
Renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, are posing a challenge to traditional fossil fuels.
Chevron’s Investments in Technology and Innovation
Chevron is investing in a range of technologies to enhance its operations and reduce its environmental impact. The company is using AI and ML to optimize its operations, developing carbon capture and storage technologies, and investing in renewable energy sources.
Opportunities and Challenges
Technological advancements create both opportunities and challenges for Chevron. Opportunities include the potential to increase production, reduce costs, and develop cleaner energy solutions. Challenges include the need to invest in new technologies, manage risks associated with technological disruption, and adapt to a changing energy landscape.
Future of the Oil and Gas Industry
The future of the oil and gas industry will be shaped by technological advancements. The industry is expected to continue to invest in technologies that can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and reduce emissions. However, the industry will also need to adapt to the growing demand for renewable energy and the increasing pressure to reduce carbon emissions.